Knee replacement surgery is a common procedure that helps people with knee pain to regain mobility and functionality in their daily lives. This surgery involves removing damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing it with a prosthetic implant. If you are considering knee replacement surgery, learn about the different types of knee replacement procedures available. This complete guide will provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision.
Definition of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing the damaged or diseased parts of the knee joint with artificial components. This surgery aims to restore the normal function of the joint and, thus, alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
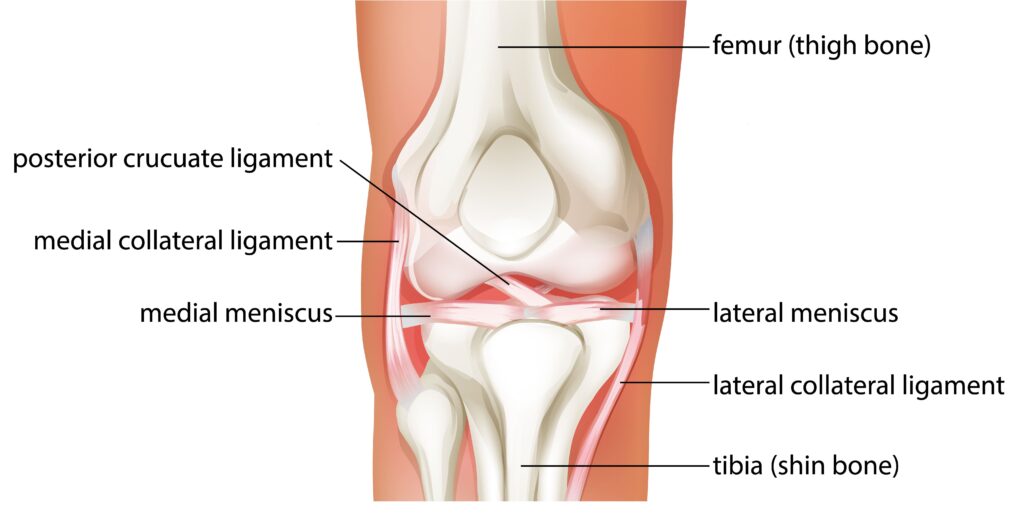
The knee joint is the largest joint in the body and is made up of three main components: the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). The femur and tibia are connected by articular cartilage, which helps to cushion and protect the bones during movement. The knee joint also contains ligaments and tendons that provide stability and support to the joint.
Indications for Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is recommended for patients with severe knee pain and limited mobility due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. Other indications for knee replacement surgery include knee deformities, such as bowleggedness and knock-knees, and knee injuries, such as ligament and meniscus tears. Patients who have tried non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy and medication without success may also be candidates for knee replacement surgery.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
There are four main types of knee replacement surgery: total knee replacement, partial knee replacement, double knee replacement, and kneecap replacement. Each type of surgery is designed to address different areas of the knee joint, depending on the extent of damage, and aims to relieve pain, restore function, and improve overall quality of life for the patient.
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves replacing the entire knee joint, including the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap), with high-quality prosthetic components made from materials like metal, ceramic, or plastic.
This surgery is the most common type of knee replacement surgery and is the preferred option for patients with severe arthritis, joint deformity, or extensive damage throughout the knee joint that significantly affects daily activities and mobility.
The surgical approach for total knee replacement can include traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques. Both approaches involve making an incision to expose the knee joint, removing damaged cartilage and bone, and implanting prosthetic components. Minimally invasive techniques use smaller incisions and specialized instruments to reduce tissue disruption, potentially leading to faster recovery and less postoperative pain.
Risks and complications associated with total knee replacement include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, prosthetic loosening or failure, and stiffness or limited range of motion. Although these risks are generally low, they can be higher in patients with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or a history of blood clots.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, involves replacing only the damaged part of the knee joint, such as the medial (inner) or lateral (outer) compartment of the knee.
It is typically recommended for patients with localized arthritis or damage that affects just one compartment of the knee and who have relatively good ligament stability.
Partial knee replacement surgery often utilizes minimally invasive techniques to minimize tissue damage and promote faster healing. The surgeon makes a smaller incision and removes only the damaged compartment of the knee joint, preserving the healthy areas. Computer-assisted or robot-assisted technologies may also be employed to enhance the precision and accuracy of the procedure.
Risks and complications for partial knee replacement are similar to those of total knee replacement but may occur at a lower rate due to the less invasive nature of the procedure. However, there is a possibility of needing a subsequent total knee replacement in the future if arthritis or damage progresses in the preserved compartments of the knee.
Double Knee Replacement
Double knee replacement, also known as bilateral knee replacement, involves replacing both knees simultaneously in one surgical procedure or sequentially during two separate surgeries in a short period of time.
This type of surgery is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis or damage in both knee joints who want to have both joints replaced at the same time to reduce the recovery time, minimize the need for multiple anaesthesia exposures, and lower overall healthcare costs.
In double knee replacement surgery, the surgical approach can be similar to that used in total knee replacement for each knee. The surgeries can be performed simultaneously or sequentially, with the latter involving two separate procedures within a short timeframe. The choice of approach may depend on factors such as the patient’s overall health, preference, and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Double knee replacement carries similar risks to total knee replacement but may have additional risks due to simultaneous or closely spaced surgeries. These risks can include increased anaesthesia exposure, prolonged immobility, and a more challenging rehabilitation process, especially if both knees are replaced simultaneously.
Kneecap Replacement
Kneecap replacement, also known as patellofemoral arthroplasty or patellofemoral joint replacement, involves replacing only the damaged kneecap and the trochlear groove in the femur (the groove in which the kneecap moves) with prosthetic components.
This type of surgery is typically recommended for patients with isolated damage or arthritis in the kneecap area, which causes significant pain and limited mobility, but who have otherwise healthy knee joint structures.
Kneecap replacement usually involves a minimally invasive approach, with a small incision made over the front of the knee. Advanced imaging techniques or computer-assisted technologies can help ensure the accurate placement of the prosthetic components.
Risks and complications specific to kneecap replacement include infection, blood clots, prosthetic dislocation or loosening, and persistent pain or instability in the patellofemoral joint. While the overall risk profile is generally lower than total knee replacement, careful patient selection and surgical technique are crucial for successful outcomes.
Robotic Knee Replacement
Dr LS Wang is a key opinion leader and trainer for robotic knee replacement. In this procedure, the surgery is done with precise assistance from a robotic arm or handheld robotic device .
Robotic Knee Replacement allows a bespoke customised knee to be planned for every patient and promises increased accuracy and precision. A robotic-assisted knee replacement offers a better balance in the soft tissues around your knee, and better aligns the joint.
Robotic-assisted procedures may also allow for enhanced recovery with shorter recovery times and better long term results.
Preoperative Evaluation and Preparation
Before undergoing knee replacement surgery, your doctor will perform a thorough evaluation to assess your overall health and the extent of your knee damage. This evaluation may involve blood tests, imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs, and physical exams. You will also need to follow specific preoperative instructions, such as stopping certain medications and preparing your home for your recovery after surgery.
Prosthetic Components
Prosthetic components used in knee replacement surgery are made from a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, and ceramic. Your surgeon will select the appropriate prosthetic components based on your specific needs and the extent of knee damage. The prosthetic components are designed to mimic the natural function of the knee joint and to withstand the forces and pressures of daily activities.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
After knee replacement surgery, you will need to follow specific postoperative care and rehabilitation instructions to ensure a successful recovery. This may include physical therapy, pain management, and activity restrictions. Follow these instructions closely to minimise complications and optimise outcomes.
Long-Term Outcomes and Considerations
Knee replacement surgery has proven to be a successful procedure in relieving knee pain and restoring mobility. However, like any surgery, there may be some risks and long-term considerations to keep in mind. These may include prosthetic component wear and tear, infection, and functional limitations.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery is a life-changing procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from severe knee pain and limited mobility. With various types of knee replacement surgeries available, including total, partial, double, and kneecap replacement, surgeons can recommend the most suitable approach based on the specific needs and extent of the patient’s knee damage.
A thorough preoperative evaluation, careful selection of prosthetic components, and adherence to postoperative care and rehabilitation instructions are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Although risks and complications are generally low, it’s important for patients to understand the long-term considerations and make informed decisions in consultation with their orthopaedic surgeon.