Ankle Ligament Tear Specialist In Singapore

Dr Wang Lushun
Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
MBBS (Singapore)
MRCS (Edin)
MMed (Ortho)
FRCS (Ortho) (Edin)
- Get active again by treating your ankle ligament
- Fellowship-trained orthopaedic surgeon
- Internationally recognised, more than 1500 surgeries performed

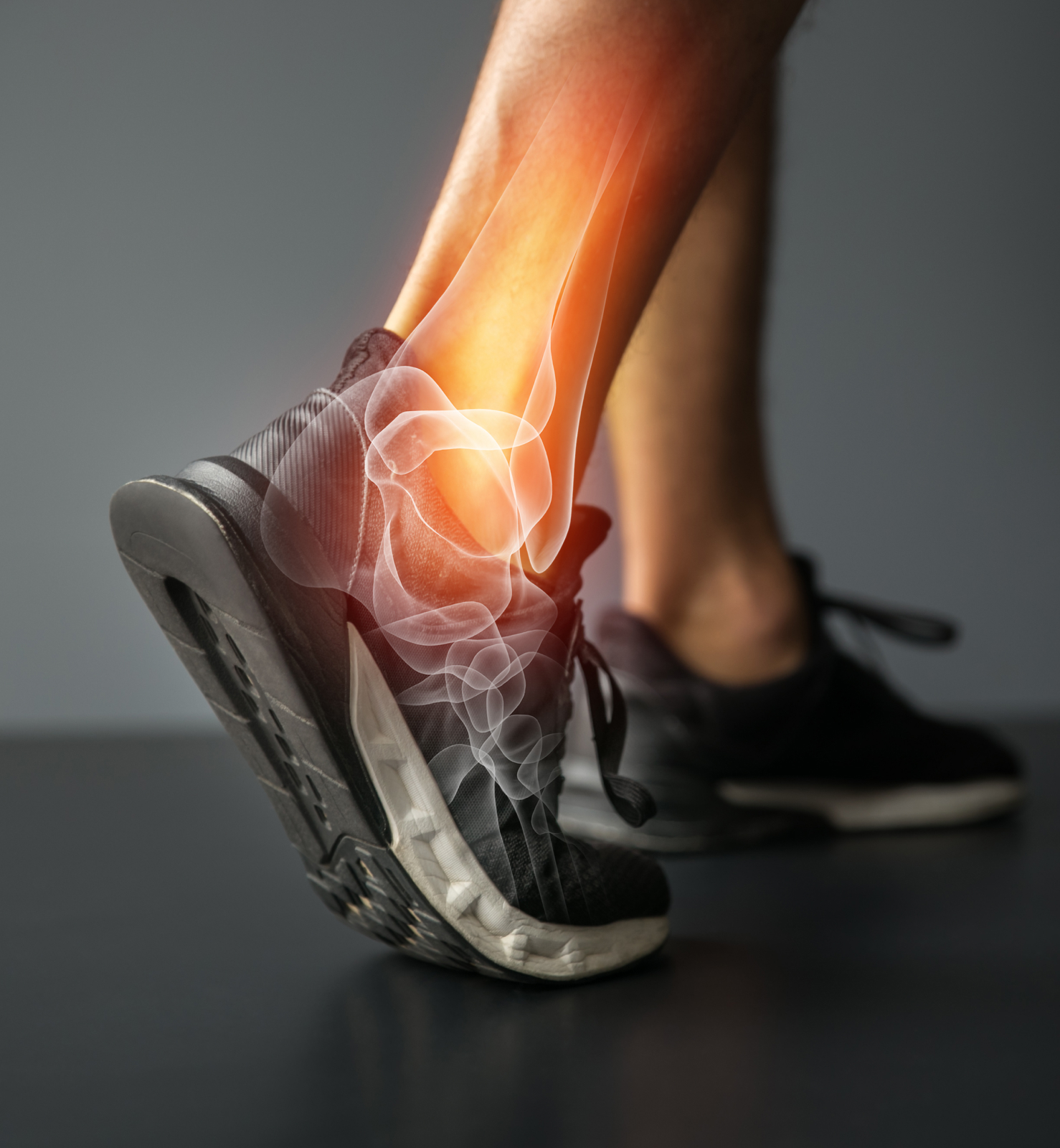
Ankle Ligament Tears Explained
Ankle ligament tears are a common injury that affects individuals of all ages and activity levels. They can be a result of a sudden twist, impact, or overuse of the ankle joint. Ankle ligament tears can be incredibly painful and debilitating, making it difficult to walk or even stand. They can also have long-lasting effects on your overall mobility and quality of life, making it essential to seek proper treatment and follow a comprehensive rehabilitation plan. In the following sections, we will break down the information you need to know about ankle ligament tears, from the causes and common types to the prevention and recovery process. Getting proper treatment for your ankle ligament will:
- Prevent further damage
- Reduce pain and swelling
- Accelerate recovery
- Minimize complications
- Regain function
Symptoms of Ankle Ligament Injuries
The symptoms of an ankle ligament injury can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. Some common symptoms include:
Pain
This is often the most noticeable symptom, with pain levels ranging from mild to severe depending on the extent of the injury.
Swelling
Inflammation and swelling around the ankle joint are common after a ligament injury.
Bruising
Discoloration of the skin around the injury site may occur as blood vessels are damaged.
Limited range of motion
The affected ankle may be difficult to move or bear weight due to pain and swelling.
Instability
A feeling of the ankle "giving way" or being unstable is common, particularly in severe sprains or complete ligament tears.
Get an accurate diagnosis
and customized treatment plan.
and customized treatment plan.
Restore your ankle’s function and stability while reducing the risk of further damage or injury.
Causes of Ankle Ligament Tears
There are several factors that can contribute to ankle ligament tears, including:
Trauma
A sudden impact or force to the ankle, such as during a fall or collision, can cause the ligaments to stretch or tear.
Twisting or rolling the ankle
This is a common cause of ankle ligament injuries, as the ligaments can become strained or torn when the ankle is forced into an unnatural position.
Overuse
Repeated stress on the ankle ligaments, such as from running or jumping, can cause them to weaken over time and become more susceptible to injury.
Poor footwear
Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or stability can increase the risk of ankle ligament injuries.
Instability or previous injury
Individuals with a history of ankle injuries, or those with naturally unstable ankles, may be more prone to ankle ligament tears.


Can a torn ankle ligament heal on its own?
Ankle ligament injuries are classified into three grades based on severity:
- Grade 1 (mild): In this case, the ligament is stretched but not torn. These injuries usually heal on their own with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications. Most individuals can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
- Grade 2 (moderate): This involves a partial tear of the ligament. Treatment for this type of injury may include immobilization in a brace or cast, along with the RICE protocol and physical therapy. Most people recover in 6 to 8 weeks, and the ligament can often heal on its own with proper care.
- Grade 3 (severe): This is a complete tear of the ligament. While some cases may heal with conservative treatment, including immobilization and physical therapy, others may require surgical intervention. Surgery might involve ligament repair or reconstruction, depending on the extent of the injury and other factors.
Overall, a torn ankle ligament has the potential to heal by itself, particularly in mild to moderate cases. However, severe cases may necessitate surgical intervention. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional, such as an experienced orthopaedic surgeon, for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
When Is The Best Time To Get Treated After An Ankle Ligament Tear?
Seeking early treatment for an ankle ligament tear is crucial in minimizing complications and promoting optimal healing. The best time to get treatment is as soon as possible after the injury occurs. Early intervention has several benefits, including:
Accurate diagnosis
A prompt evaluation by an orthopaedic surgeon,sports medicine specialist, or ankle ligament tear specialist in Singapore, can help determine the severity of the injury (Grade 1, 2, or 3) and guide appropriate treatment.
Reduced inflammation
Application of the RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can help manage pain, minimize swelling, and promote healing.
Better functional outcomes
Early intervention, including immobilization (if necessary) and a structured rehabilitation program, can reduce the risk of chronic instability, recurrent sprains, and long-term complications like arthritis.
Faster return to activity
Timely treatment can help patients return to their daily activities and sports more quickly and safely.
Delaying treatment for an ankle ligament tear may lead to complications such as chronic pain, instability, and a higher likelihood of re-injury.
Can I Use Medisave For Ankle Ligament Tear Treatment?
Yes you can use Medisave to offset the cost of ankle ligament tear treatments.
Reach out to us today to learn more about payment options.
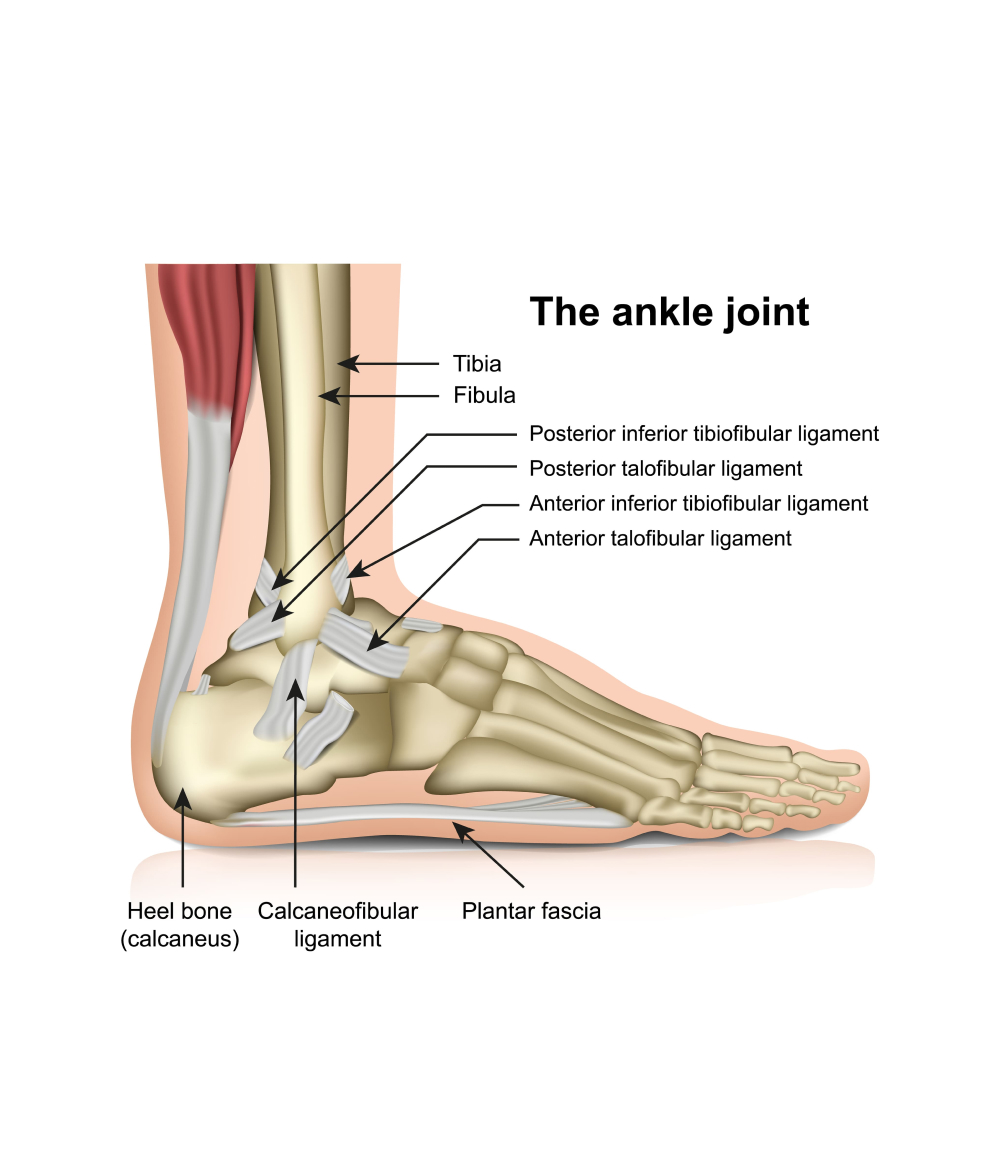
Anatomy of the Ankle Ligaments
The ankle joint is a complex structure that consists of bones, tendons, and ligaments. The ligaments in the ankle help to stabilize the joint, connecting the bones and allowing for smooth movement. There are several important ligaments in the ankle, including:
- The lateral ligaments, which are located on the outer side of the ankle and consist of three separate ligaments: the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and the posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL).
- The medial or deltoid ligament, located on the inner side of the ankle and consists of several smaller ligaments that work together to provide stability.
- The syndesmotic ligaments, which connect the two lower leg bones (the tibia and fibula) and help to stabilize the ankle joint.
Understanding the anatomy of the ankle ligaments is crucial to recognizing the causes and symptoms of ankle ligament tears, as well as guiding the treatment and rehabilitation process.
Causes of Ankle Ligament Tears
There are several factors that can contribute to ankle ligament tears in Singapore, including:
- Trauma: A sudden impact or force to the ankle, such as during a fall or collision, can cause the ligaments to stretch or tear.
- Twisting or rolling the ankle: This is a common cause of ankle ligament injuries, as the ligaments can become strained or torn when the ankle is forced into an unnatural position.
- Overuse: Repeated stress on the ankle ligaments, such as from running or jumping, can cause them to weaken over time and become more susceptible to injury.
- Poor footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or stability can increase the risk of ankle ligament injuries.
- Instability or previous injury: Individuals with a history of ankle injuries, or those with naturally unstable ankles, may be more prone to ankle ligament tears.
Common Types of Ankle Ligament Tears
There are several different types of ankle ligament tears, which are classified based on the severity of the injury and the affected ligament:
- Sprains: A sprain is a stretch or partial tear of the ligaments, which is the most common type of ankle ligament injury. Sprains can range in severity from mild (Grade I) to moderate (Grade II) to severe (Grade III), with the latter often involving a complete tear of the ligament.
- Lateral ligament injuries: These are the most common type of ankle ligament tear, typically involving the ATFL and/or the CFL. Lateral ligament injuries often occur when the foot rolls inward (inversion injury).
- Medial ligament injuries: Although less common, medial ligament injuries can occur when the foot rolls outward (eversion injury) or from a direct impact to the inner side of the ankle.
- Syndesmotic injuries: Also known as a “high ankle sprain,” these injuries involve the ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula. They are often caused by a twisting motion or impact to the lower leg.
Diagnosing Ankle Ligament Tears
Diagnosis of an ankle ligament tear typically begins with a physical examination by a healthcare professional, who will assess the ankle's range of motion, check for swelling and bruising, and perform specific tests to determine the severity of the injury. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the damage to the ligaments.
Receiving an accurate diagnosis will guide the treatment and rehabilitation process, ensuring the best possible outcome for your ankle injury.
Treatment Options for Ankle Ligament Injuries
The treatment for ankle ligament tears depends on the severity of the injury and the specific ligament(s) affected. The primary goals of treatment are to manage pain and swelling, protect the injured ligaments, and promote healing. Some common treatment options include:
RICE protocol
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation are the first steps in treating an ankle ligament injury, helping to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen, can help manage pain and inflammation.
Bracing or immobilization
Wearing a brace or using crutches can help protect the injured ligament and allow it to heal.
Physical therapy
A physical therapist can guide you through exercises and stretches to help restore strength, flexibility, and stability to the ankle joint.
Surgery
In severe cases, particularly those involving complete ligament tears or chronic instability, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged ligament(s).
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
The rehabilitation process for an ankle ligament tear is essential to restoring the strength, flexibility, and stability of the ankle joint. A comprehensive rehabilitation program will typically include:
- Range of motion exercises: These exercises help to restore normal movement to the ankle joint.
Strengthening exercises: Targeting the muscles surrounding the ankle can help to support and stabilize the joint. - Balance and proprioception exercises: These exercises help to improve your awareness of your ankle’s position and movement, which can reduce the risk of future injuries.
- Functional exercises: As you progress in your recovery, more advanced exercises can be introduced to simulate the demands of your daily activities or sport.
The recovery timeline for an ankle ligament injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the specific ligament(s) affected, and your individual healing process. In general, mild to moderate sprains may take several weeks to heal, while severe sprains or complete ligament tears may take several months or longer.
Preventing Ankle Ligament Tears
While it may not be possible to completely prevent ankle ligament injuries, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Warm-up and stretch: Before engaging in physical activity, take the time to warm up your muscles and stretch your ankle joint.
- Strengthen your ankles: Regularly practising ankle-strengthening exercises can help to support and stabilize the joint, reducing the risk of injury.
- Wear proper footwear: Choose shoes that provide adequate support and stability, particularly when engaging in sports or activities that place stress on the ankle joint.
- Avoid uneven surfaces: When possible, avoid running or walking on uneven terrain, which can increase the risk of ankle injuries.
- Listen to your body: If you feel pain or discomfort in your ankle, stop the activity and allow your body time to rest and recover.


Dr Wang Lushun
Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
MBBS (Singapore)
MRCS (Edin)
MMed (Ortho)
FRCS (Ortho) (Edin)
Internationally Recognised & Double Fellowship-Trained Surgeon With Over 18 Years of Experience
- Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS),
National University of Singapore - Member of The Royal College of Surgeons (MRCS),
Edinburgh, United Kingdom - Master of Medicine in Orthopaedic Surgery (MMed),
National University of Singapore - Fellow of The Royal College of Surgeons in Orthopaedics and Traumatology (FRCS), Edinburgh, United Kingdom
As a Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon and former Head of the Hip and Knee Division in Ng Teng Fong Hospital, he has won awards for superior patient outcomes (value driven), service quality and enhanced recovery programmes. His patients include current and former national athletes and sporting professionals.
Why Choose
Dr Wang Lushun?
Trusted
Leadership on Orthopaedic Advisory Boards
Skilful
Double Fellowships at Centres of Excellence
Experienced
Senior Consultant with Over 18 Years of Experience
Patient-Centred Orthopaedic Care
We are dedicated to your recovery and well-being. Every patient deserves the freedom that comes with active living. Whether you're an athlete sidelined by an injury or a weekend hobbyist desperate to return to your passion, our mission is to help you regain your mobility and independence.
Personalised Approach For Positive Outcomes
Our clinic prioritizes time dedicated to understanding each patient’s injuries and needs. Dr Wang strongly believes that personalised care & patient management will lead to better outcomes & positive experiences.
Minimally Invasive Techniques For Faster Recovery
Dr Wang’s extensive experience with minimally invasive procedures allows for less scarring, lower risk of complications and faster recovery compared to traditional surgical methods.
Aftercare Focused On Restoring Mobility & Well-Being
As an avid sportsperson, Dr Wang understands the time and patience required to regain mobility and return to active living. After your procedure is completed, Dr Wang will make sure your recovery is smooth and comfortable.
Insurance
We accept all patients, with or without insurance plans. Additionally, we are on the specialist panels of these Health Networks/Insurance Plans. Please contact us if you have any queries and we will be happy to assist you in checking with your insurance provider.