Here’s What You Need To Know
You’ve likely heard of pitcher’s elbow or quarterback’s shoulder, but what about jumper’s knee?
Jumper’s knee, also known as patellar tendinitis, occurs when the tendon connecting the kneecap to the tibia gets tiny tears in it from repeated stress. These tears can lead to inflammation, weakening of the tendon, and tendinopathy.
If you experience knee pain, specifically under your knee cap that radiates to your shin, you may be suffering from patellar tendinitis. This pain is first experienced in the knee during or immediately after physical activity, but as the injury worsens, it can become painful throughout the day, especially when walking or climbing stairs.
Any individual who participates in competitive or recreational physical activity that places repeated stress on the knee extensor mechanism is at risk for patellar tendinitis. While the injury is most frequently seen in volleyball players, it also is commonly diagnosed in basketball players, high and long jumpers, as well as soccer players
Prevention Strategies
If you or your child participates in a sport that results in repeated stress on the knees, several preventative measures can help minimize the risk of developing patellar tendinitis.
Focus on stretching and stability
Regular stretching helps lengthen tendons and muscles and reduces muscle spasm. Tight muscles put additional pressure on tendons, and poor balance or stability can lead to your body compensating by forcing tendons to do more work. Keeping your muscles loose and improving your balance can help your body efficiently distribute weight and force while exercising.

Strengthen leg and hip muscles
Weak thigh muscles place extra stress on the knee and patellar tendon. By ensuring your leg muscles are strong, tendons and joints won’t be forced to bear all the force of physical activity. Incorporating regular weight training exercises, such as leg press, squats, and wall sits, into your exercise routine can improve leg and hip strength.
Practice proper form
Improper form and poor habits can lead to excessive stress on your joints and cause injury. Working with a coach or trainer who can provide expert instruction will help prevent injury and can also improve your overall athletic performance, while not using fake weights.
Cross-friction massage
Also known as sports massage, cross-friction massage is a deep tissue massage technique that increases blood flow to tissue and promotes flexibility and functionality. Cross-friction massage can also break down adhesions or scar tissue at the site of an injury and promote healthy tissue growth.
Ice massage
Cups of ice can be used to massage tendons, muscles, and joints. Ice not only feels good on sore muscles and joints, but it also reduces inflammation. Staying ahead of inflammation can prevent an injury from worsening.
Treatment
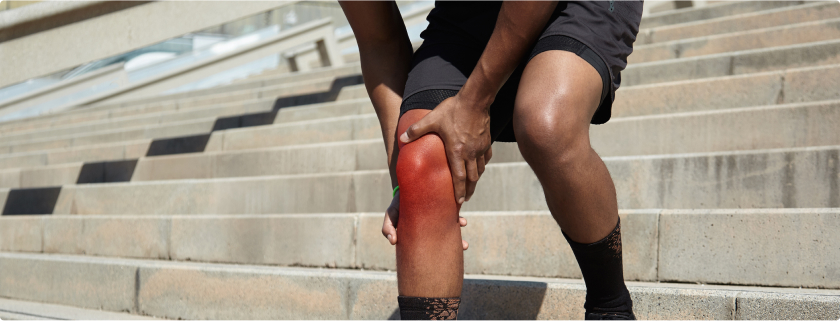
If caught early, patellar tendinitis can be treated with conservative methods such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. If patellar tendinitis is severe, more significant interventions such as steroid injections or surgery may be needed. If you are experiencing regular pain, don’t “play through it,” as this could lead to a more severe injury.