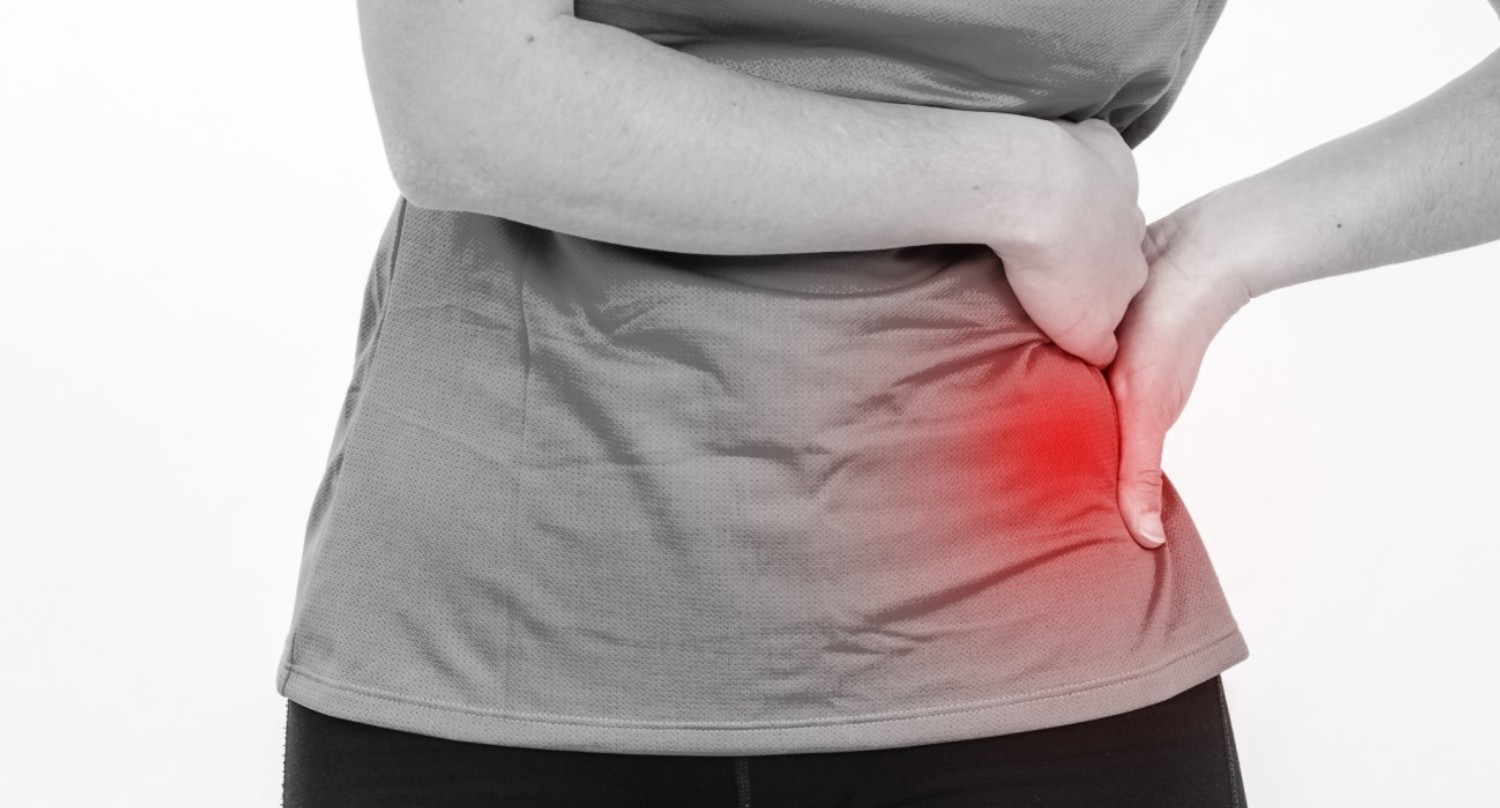
What is Hip Osteoarthritis?
Hip Osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative joint disease, involves the breakdown of cartilage, the cushioning tissue between bones in the hip. This condition typically develops gradually and results in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the hip joint. The exact cause of hip OA is not fully understood, but factors such as age, genetics, joint injury, and obesity are known contributors.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Non-pharmacological treatments play a vital role in managing hip osteoarthritis, focusing on alleviating symptoms and improving joint function without medication. Key approaches include:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist help strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Weight Management: For overweight individuals, weight loss can significantly decrease the stress on the hip joint, thereby reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Assistive Devices: Using walking aids like canes or walkers can help in distributing weight away from the affected hip, reducing pain and improving stability.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat can relax muscles and improve circulation, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the painful area.
These treatments are often recommended as initial steps in managing hip OA and can be combined with other therapies for greater effectiveness.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments for hip OA involve the use of medications to alleviate pain and inflammation. Common options include:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen are often the first line of treatment for managing mild to moderate hip pain.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen reduce inflammation and relieve pain. They are available over the counter and in stronger prescription forms.
- Topical Medications: Creams, gels, and patches containing pain-relieving substances can be applied directly to the hip to reduce pain with fewer systemic side effects.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injected directly into the hip joint, corticosteroids can provide significant pain relief and reduce inflammation. However, the number of injections one can receive is limited due to potential side effects.
- Viscosupplementation: This involves injecting hyaluronic acid into the hip joint to improve lubrication and reduce pain, although its effectiveness can vary.
Surgery
Surgery may be considered for hip osteoarthritis when other treatments have not provided sufficient relief. The most common procedures include:
- Hip Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive surgery involves small incisions and the use of a camera to diagnose and sometimes treat hip problems. It can be used to remove loose bodies or repair a torn labrum, potentially relieving some symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Osteotomy: In an osteotomy, the bones of the hip joint are cut and realigned to redistribute weight and reduce pain. This procedure is more common in younger patients with early-stage osteoarthritis.
- Total Hip Replacement (Arthroplasty): This involves replacing the damaged hip joint with artificial components. It is a major surgery typically recommended for advanced osteoarthritis, providing significant pain relief and improved mobility.
- Hip Resurfacing: This is a less common alternative to total hip replacement that involves capping the femoral head with a metal prosthesis, preserving more of the bone.
The decision to undergo surgery depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, level of pain, mobility, and overall health.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
Lifestyle modifications and home remedies are important aspects of managing hip OA, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, or walking can help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
- Proper Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and manage body weight.
- Adequate Rest: Getting enough sleep and rest is crucial for managing pain and fatigue associated with osteoarthritis.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress, which may exacerbate pain.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Making changes to the living and work environment, such as using ergonomic chairs and placing frequently used items within easy reach, can help reduce strain on the hip joint.
These lifestyle changes, when combined with medical treatments, can significantly impact the management of hip OA symptoms.
Conclusion
Each treatment option for hip OA offers different benefits and may be more suitable for certain stages of the condition or individual patient needs. Consult with your orthopaedic surgeon to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific symptoms and lifestyle.